Often we look to certain symbols in Excel that are hard to locate on the keyboard. Or the opposite – we look to find the Excel character codes for certain characters. In such cases we must usually revert to using the CHAR Excel function or the CODE Excel function. Let us explore these functions and how to use them both in Excel and VBA today.
Excel Character Codes
First let us start with exploring the Excel Character codes.
The table below represent the full default encoding in Excel:
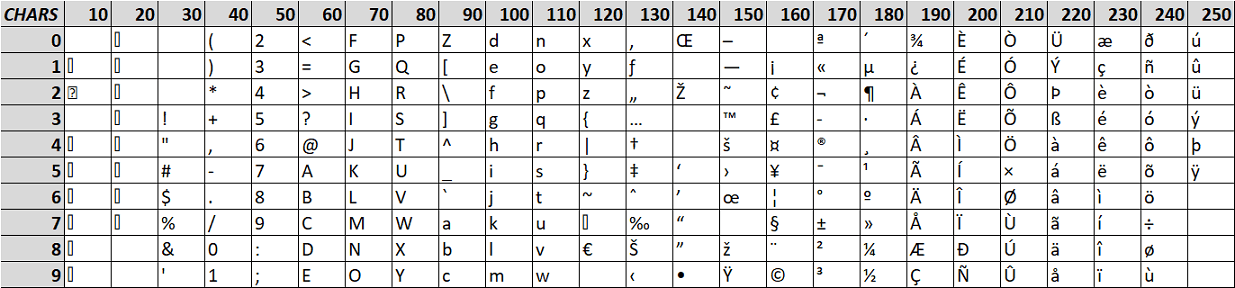
On the right side is the Excel character (CHAR) and on the left you have the numeric representation (CODE) of the character.
Converting Characters to Codes (Excel CODE function)
The Excel CODE function allows you to easily obtain the numeric code for the provided character (1 character string).
Syntax
The syntax for the CODE function in VBA is:
1 | CODE( string ) |
Parameters
string
A single character string.
Example usage
Excel
Below example of using the Excel CODE function:

VBA
Below VBA equivalent of the Excel CODE Funtion – the Asc function
1 2 | Debug.Print Asc("<")'Result: 60 |
Converting Codes to Characters (Excel CHAR function)
The Excel CHAR function allows you to easily obtain the character represented by the numeric code.
Syntax
The syntax for the CHAR function in Excel is:
1 | CHAR( number) |
Parameters
number
A number from 0-255.
Example usage
Excel
Below example of using the Excel CHAR function:

VBA
Below VBA equivalent of the Excel CHAR Funtion – the Chr function:
1 2 | Debug.Print Chr(60)'Result: < |